Data encryption is a process that protects sensitive data and is crucial in our digital age. There are several encryption methods designed for different types of data. In this article, we will explore three states of data and ways to protect it securely. Follow along!
What is Data Encryption?
From ancient times, people turned messages into codes (or ciphertext) to protect the hidden information. The only way to read it was to find the key to decode the text. This approach is used nowadays and is called data encryption.
Encryption algorithms are constantly being developed to provide secure protection for sensitive data and address modern threats. Additionally, numerous data protection regulations control how personal data is managed. For instance, Europe's leading data security regulation is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
There are two types of data encryption:
- Symmetrical encryption, which uses the same key for both encrypting and decrypting data. It is widely used in multiple applications, including VPNs, file sharing, data storage, and more.
- Asymmetrical encryption, which involves a pair of keys: a public key and a private key. This type of encryption is used in different contexts than symmetrical encryption, such as for digital signatures and blockchains.
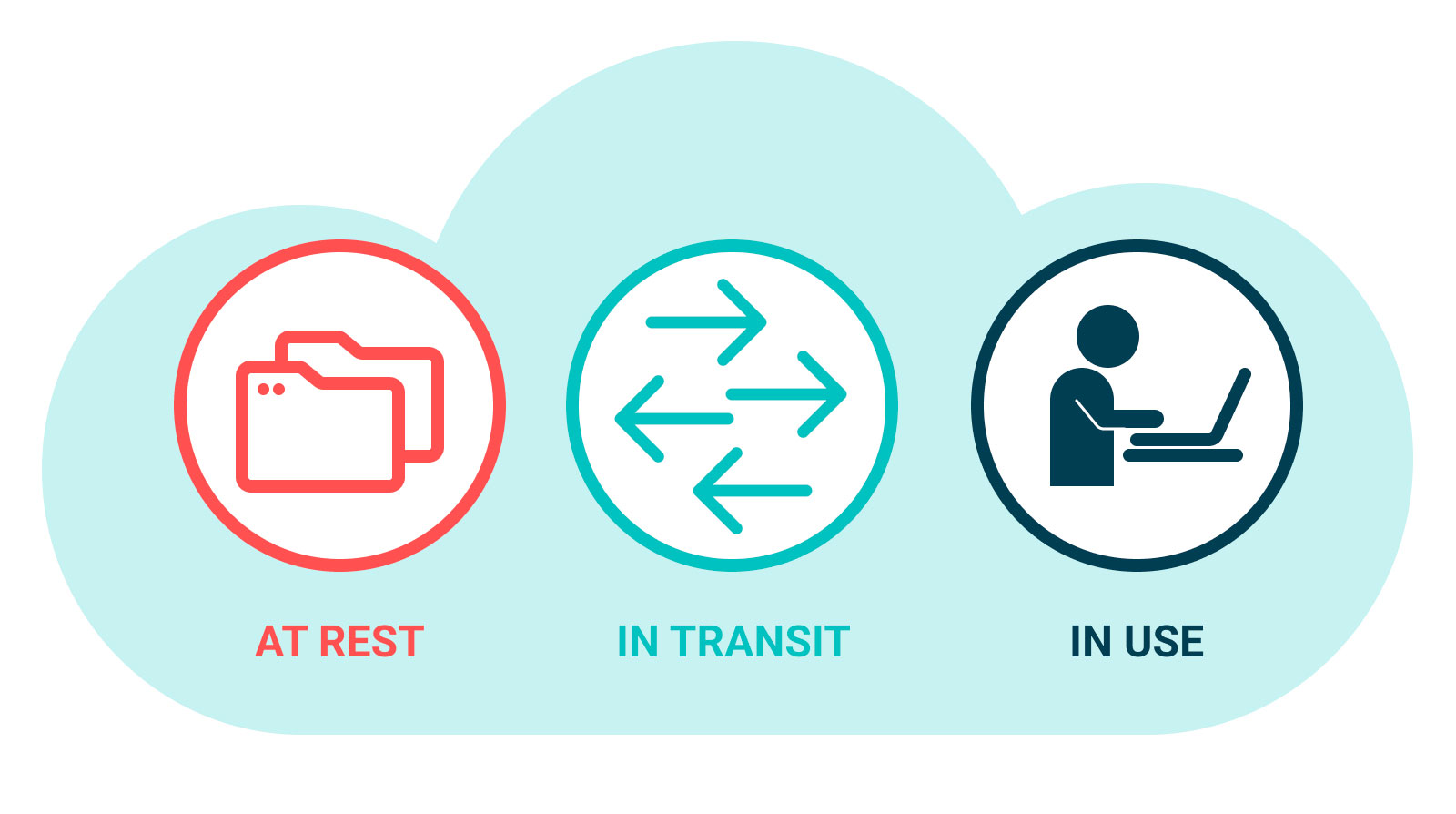
The States of Data: Data at Rest vs. Data in Transit vs. Data in Use
To effectively protect encrypted data, it is crucial to understand its state. There are three states: data at rest, data in transit, and data in use. Let's look closely at each.
Data at Rest
Data at rest is a term related to data that is stored on computer storage media and is not transferred or accessed, such as data on a hard drive, databases, archives, etc.
This data is usually an appealing goal for hackers as it may include sensitive information. However, due to restricted access, data at rest might be considered less vulnerable than data in transit.
How to Protect Data at Rest?
To protect this type of data, you need to encrypt all stored data, control access permissions, regularly create backups and store them in safe physical places, implement firewalls, security patches and updates, etc.
Data in Transit
Data in transit (also called data in motion) refers to data being transferred between locations, such as devices within a local network or through the Internet. Depending on whether the network is public or private, data in transit is categorized into two types.
This data type includes information sent via email or messengers, live streams or video calls, e-commerce transactions, etc.
How to Protect Data in Transit?
When transferred over networks, data is at risk of exposure to third parties. Therefore, data should be encrypted, preferably using end-to-end encryption. This way, only the sender and recipient have a key to decrypt the message; moreover, no other parties can read it even in case of data interception.
Data in Use
Data in use is data that is being edited, accessed, and processed by users or applications. Examples include opened documents, real-time analytics programs, and data processed by CPUs or stored in memory (RAM).
Protecting data in use is crucial as it is vulnerable to data breaches and third-party access. Moreover, if hackers intercept and compromise the data, they can access both data at rest and data in transit.
How to Protect Data in Use?
As with other data types, encrypting data in use is essential for data loss prevention. Additionally, other protection methods should be used, such as continuous user authentication, access permissions management, and non-disclosure agreements.
Best Practices of Data Encryption
Encryption plays a crucial role in data protection. Let's explore the practices that help to manage data access and prevent breaches:
- Categorize the data based on its state, sensitivity, risk profile, and regulatory requirements. That will help you choose the most effective protection methods, ensuring safety for all data types.
- Implement basic protection tools. Firewalls, strong authentication methods, and identity and access management (IAM) are relatively easy to implement and play a crucial role in protecting data.
- Use automated control. Some tools automatically block malicious files and users and encrypt data to reduce the risk of compromising it.
- Provide full disk encryption. It is done to protect data when the device is lost or stolen. With full disk encryption, hackers will not be able to access data stored on the laptop or smartphone.
- Implement data loss prevention (DLP) solutions. These solutions monitor data to detect potential leaks at all data states and prevent breaches.
- Protect cloud storage. Use cloud access security brokers (CASBs) that help keep information on the cloud safe.
- Use mobile device management (MDM) practices to protect corporate data. MDM software helps control all the company's devices, including not only computers but also mobile devices.
Trends in Data Encryption
The sphere of data protection is constantly evolving to resist hacker threats. Here are some current data encryption trends that are expected to grow in the future:
End-to-End Encryption
It ensures the data is encrypted while it is transferred between the sender and the recipient, thereby preventing hackers from accessing the data while it is in transit. Even if data is intercepted during transmission, it remains unreadable to unauthorized parties.
Encryption as a Service (EaaS)
Implementing cloud-based solutions for data encryption is becoming common. These solutions provide data protection for all data states and are convenient for companies and governmental organizations.
Bring Your Own Encryption (BYOE)
With BYOEs, people can manage their encryption keys independently, ensuring full control over their data privacy. To decrypt data, clients need to use their key to restore the original message.
Field-level encryption
This method encrypts certain fields of a page on the client side, such as payment details, passwords, and health information. Thus, server providers don't have access to this data.
Sequential Link Encryption
This method encrypts data at each communication link or hop in a network, providing enhanced security by preventing unauthorized access at any point of data transmission.
Data Erasure is a Part of Data Protection
The last but crucial step of data protection is data sanitization. When data is no longer needed and the device changes owners, all data must be securely deleted to prevent unauthorized access and potential data breaches. Manual deletion is not an option as it is time-consuming and leaves data remnants.
To ensure that data is 100% deleted, use certified solutions. NSYS Data Erasure is software designed for the used device industry. It allows you to wipe data from multiple mobile phones and tablets simultaneously by connecting up to 60 devices to one PC at once.
Moreover, NSYS Data Erasure wipes data in compliance with international standards and regulations, including ADISA, NIST SP 800-88, GDPR, and R2.
Click the button below and try NSYS Data Erasure for your business!








